About Algorithms
SELECTION SORT
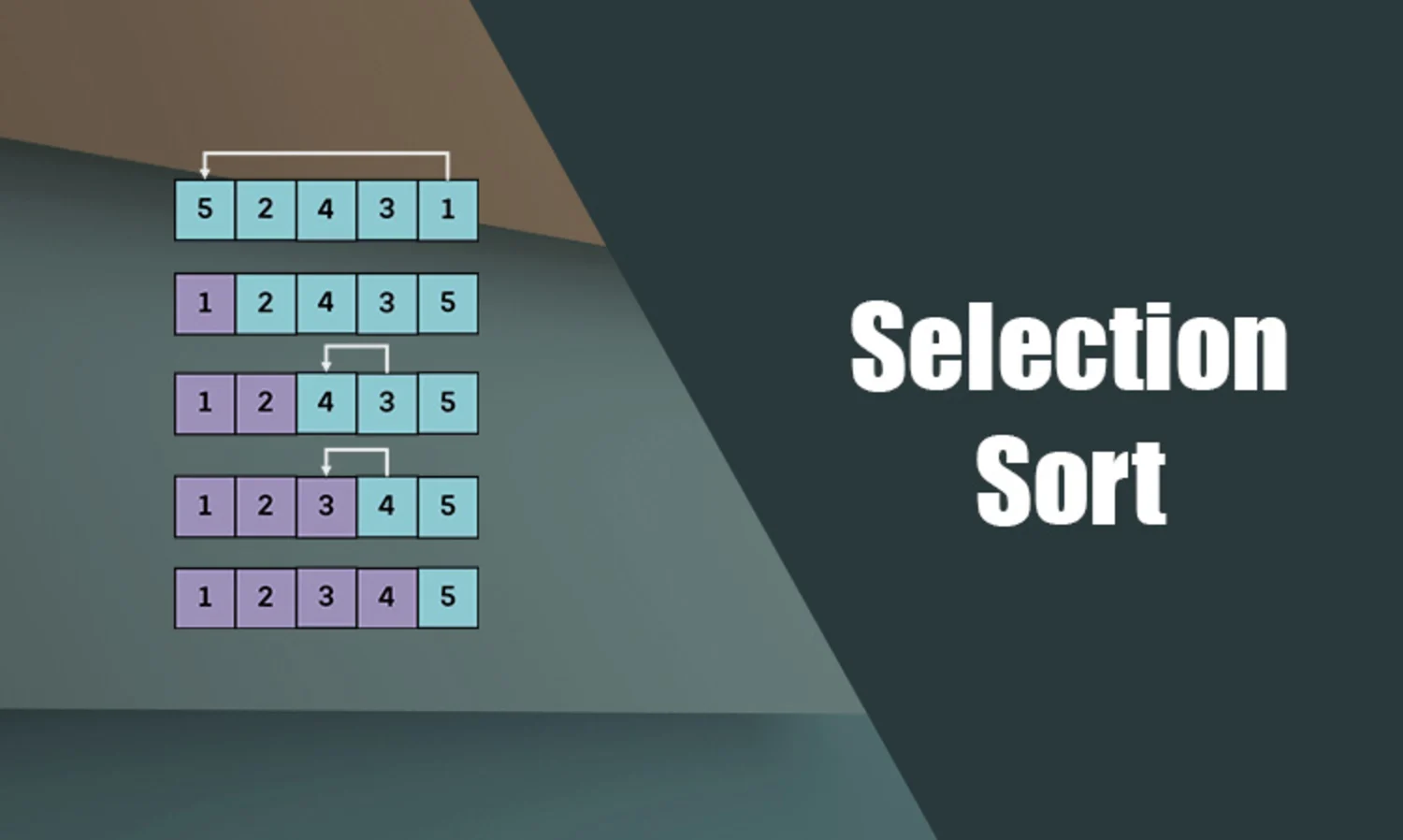
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted part and putting it at the beginning.
The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array :
- The subarray which already sorted.
- The remaining subarray was unsorted.
Complexity Analysis of Selection Sort:
Time Complexity: The time complexity of Selection Sort is O(N2) as there are two nested loops: Therefore overall complexity = O(N) * O(N) = O(N*N) = O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1) as the only extra memory used is for temporary variables while swapping two values in Array. The selection sort never makes more than O(N) swaps and can be useful when memory write is a costly operation
INSERTION SORT
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works similar to the way you sort playing cards in your hands. The array is virtually split into a sorted and an unsorted part. Values from the unsorted part are picked and placed at the correct position in the sorted part.
Characteristics of Insertion Sort:
- This algorithm is one of the simplest algorithm with simple implementation.
- Basically, Insertion sort is efficient for small data values.
- Insertion sort is adaptive in nature, i.e. it is appropriate for data sets which are already partially sorted.
Complexity Analysis of Selection Sort:
Time Complexity: O(N^2) Auxiliary Space: O(1)
BUBBLE SORT
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order. This algorithm is not suitable for large data sets as its average and worst-case time complexity is quite high.
Worst Case Analysis for Bubble Sort:
- The worst-case condition for bubble sort occurs when elements of the array are arranged in decreasing order.
Complexity Analysis of Selection Sort:
Time Complexity: O(N^2) Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Codes
Executable codes
- All
- Selection Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Insertion Sort